
Search
Multidimensional Poverty Index Report 2019: Seychelles

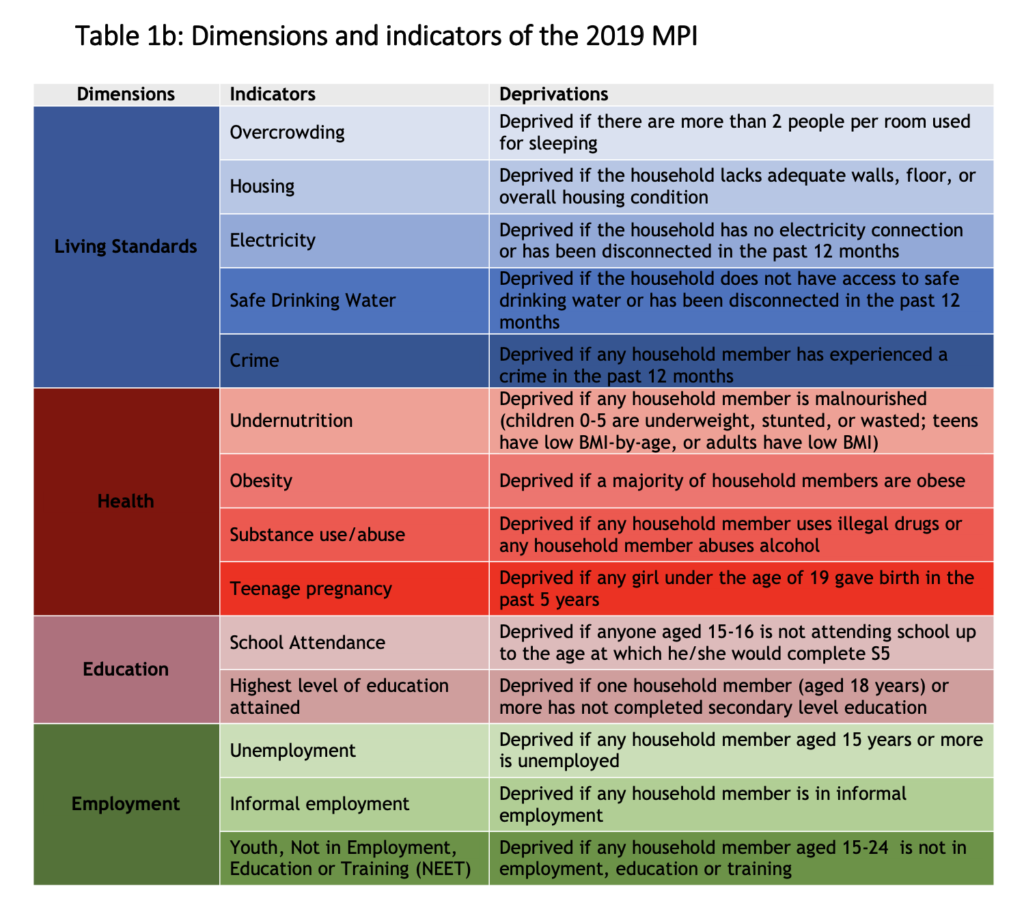
This report presents the findings of the national MPI for Seychelles. The Seychelles MPI was developed by the Poverty Alleviation Department and the National Bureau of Statistics of Seychelles with technical support from the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI). As a high-income country, and a Small Island Developing State, the challenges faced by Seychelles in poverty reduction are different from other contexts. Seychelles’ MPI, which includes innovative indicators on obesity, substance abuse and crime, can help policymakers identify those being left behind and target their programmes more effectively.
Executive Summary
In the third quarter of 2019, the poverty incidence (H) was 11.88%, and the average intensity (A) was 33.26%. The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), which is the product of H and A (H*A) was 0.040.
Examining the poverty indices by different subgroups reveal interesting results. It has been found that those living in the largest households, may be more likely to experience multidimensional poverty (with a headcount ratio of 31.15%), than those living in the smallest households (with a headcount ratio of 4.89%). In fact, the relationship between household size and multidimensional poverty is quite clear: poverty rate increases, as the household size increases.
A breakdown of the poverty indices by age group also shows interesting results. The poverty rate (16.46%) and MPI (0.057) is highest for those in the youth age group. The youth are particularly affected by ‘Overcrowding’, ‘Substance use/abuse’, ‘School attendance’ and ‘Youth NEET’.
With regards to labour force status, the results show that as expected, multidimensional poverty is more prevalent among the unemployed (with a headcount ratio of 57.35%), than among those who are employed and those who are outside the labour force.
The report also examines performance across characteristics of household head. With regards to sex of the head of household, results show that the incidence of multidimensional poverty is higher among female-headed households (with a rate of 12.88%), than male-headed households (with a rate of 10.40%).
An obvious gradient can be observed in the headcount ratio by education level of head of household: the lower the education level (no schooling), the higher the headcount ratio (34.58%). The same pattern can be observed in the MPI, whereby those with no schooling, has the highest MPI (0.115), and the MPI decreases as the education level increases.
Poverty indices were also examined at island level. Results show that the main island (Mahe), experiences a higher rate of multidimensional poverty (12.2%), than the Inner islands (7.41%). The MPI follows the same pattern, whereby an MPI of 0.041 is observed for Mahe, whereas a lower MPI of 0.022 is observed for the Inner islands.
Seychelles Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)
Source: Seychelles MPI Report.
This report is available here.
















